rectifier
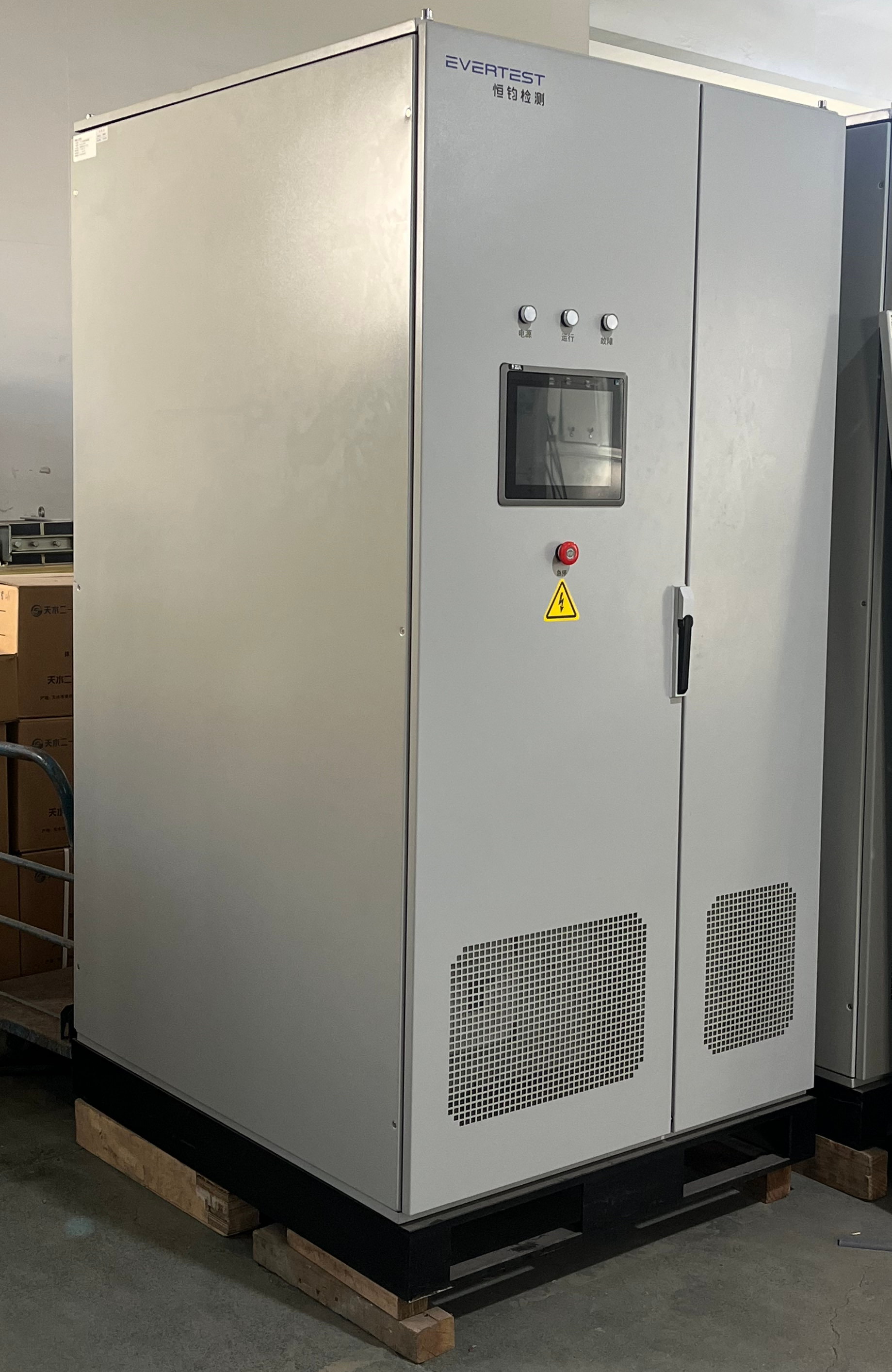
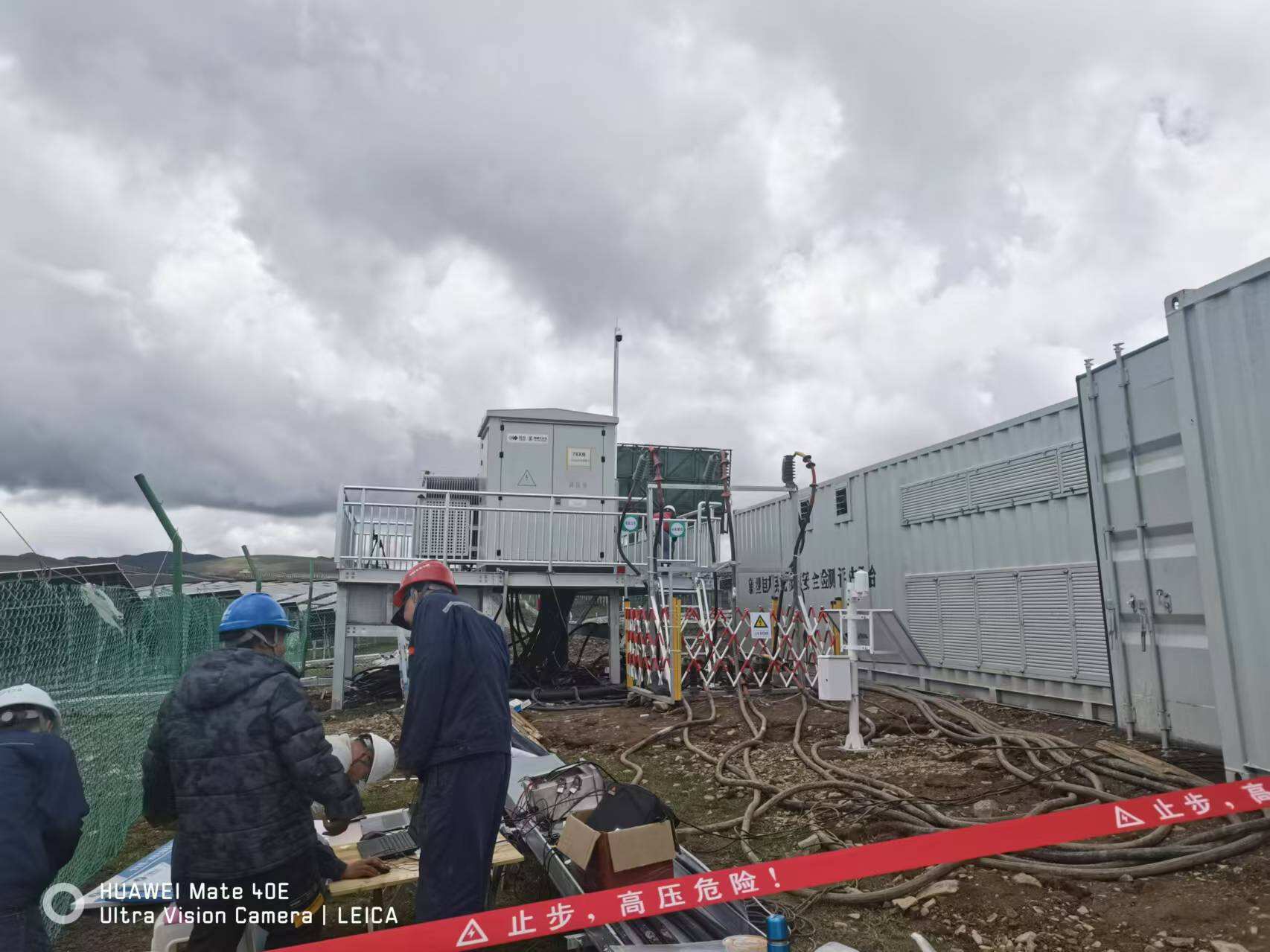
A rectifier is a fundamental electronic device that converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), serving as a crucial component in modern power electronics. This sophisticated device employs semiconductor components, typically diodes or thyristors, to allow current flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. Modern rectifiers come equipped with advanced filtering systems that smooth out voltage ripples, ensuring a stable DC output essential for powering electronic devices. The technology incorporates various configurations, including half-wave, full-wave, and bridge rectifiers, each designed to meet specific power conversion requirements. These devices are integral in numerous applications, from small-scale consumer electronics to large industrial power supplies. Rectifiers feature protective mechanisms against voltage surges and overheating, incorporating thermal management systems and overcurrent protection. Their efficiency ratings typically range from 85% to 98%, depending on the design and application. In industrial settings, rectifiers play a vital role in motor drives, electroplating processes, and uninterruptible power supplies. The technology continues to evolve with improvements in semiconductor materials and circuit designs, leading to more compact, efficient, and reliable power conversion solutions.