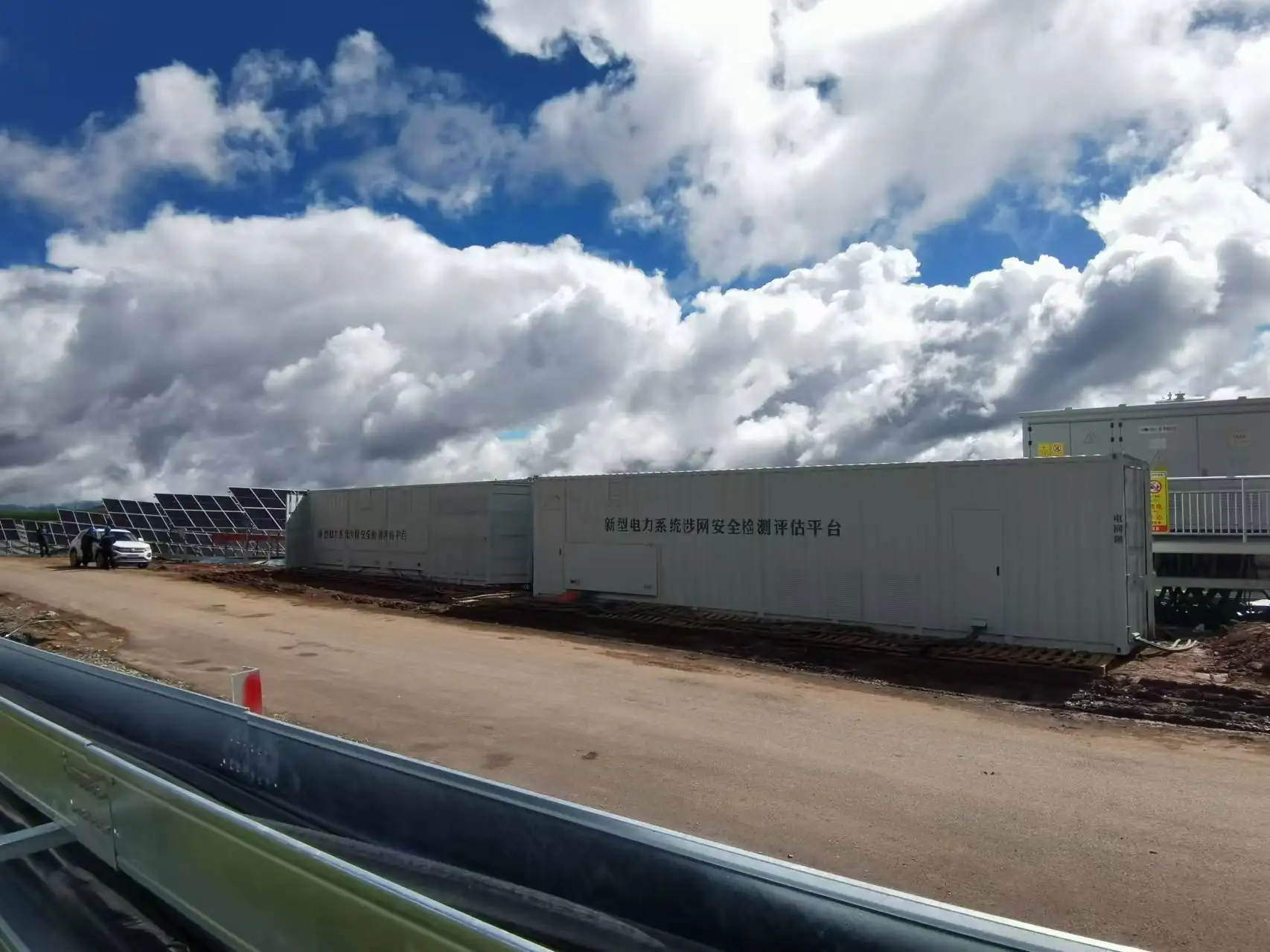
Power plant stability testing has become increasingly critical as electrical grids worldwide face mounting challenges from renewable energy integration, aging infrastructure, and growing demand. Traditional testing methods often fall short in providing comprehensive analysis of grid behavior under various disturbance scenarios. A regenerative grid simulator offers an advanced solution that revolutionizes how power plants conduct stability assessments, providing unprecedented accuracy and efficiency in testing protocols. This innovative technology enables engineers to evaluate grid performance under controlled conditions while minimizing risks and operational disruptions.
The evolution of power grid testing technology has reached a pivotal moment where conventional approaches struggle to meet modern requirements. Engineers and technicians need sophisticated tools that can replicate real-world grid conditions while maintaining safety standards and operational integrity. The regenerative grid simulator represents a breakthrough in testing methodology, offering capabilities that extend far beyond traditional static testing equipment.
Understanding Regenerative Grid Simulation Technology
Core Principles of Grid Simulation
A regenerative grid simulator operates on advanced power electronics principles that enable precise control over electrical parameters including voltage, frequency, phase angle, and harmonic content. Unlike conventional testing equipment that merely applies predetermined load patterns, this technology dynamically responds to grid conditions and can simulate complex disturbance scenarios. The regenerative aspect allows the system to feed energy back into the grid or testing circuit, significantly improving efficiency and reducing operational costs.
The fundamental architecture of a regenerative grid simulator incorporates sophisticated control algorithms that monitor and adjust electrical parameters in real-time. These systems utilize high-speed digital signal processing to maintain precise control over output characteristics while simultaneously analyzing feedback from the power plant under test. This bidirectional energy flow capability distinguishes regenerative systems from traditional testing equipment and enables more comprehensive stability assessments.
Advanced Control Systems
Modern regenerative grid simulator systems employ state-of-the-art control technologies including model predictive control, adaptive algorithms, and machine learning integration. These advanced control systems enable the simulator to predict grid behavior and adjust testing parameters proactively rather than reactively. The integration of artificial intelligence allows for continuous optimization of testing protocols based on historical data and emerging grid conditions.
The control system architecture typically includes multiple layers of protection and monitoring capabilities that ensure safe operation while maximizing testing effectiveness. Real-time data acquisition systems capture thousands of measurements per second, providing engineers with detailed insights into power plant performance under various stress conditions. This comprehensive data collection enables more accurate modeling and better understanding of grid stability characteristics.
Enhanced Stability Testing Capabilities
Dynamic Response Analysis
Traditional stability testing often relies on static load conditions or simple step changes that fail to capture the dynamic nature of real grid disturbances. A regenerative grid simulator can generate complex disturbance patterns that accurately replicate actual grid events including frequency deviations, voltage sags, harmonic distortion, and transient conditions. This enhanced capability allows engineers to evaluate power plant response under realistic operating scenarios.
The dynamic response analysis capabilities of regenerative systems extend to modeling interconnected grid behaviors where multiple power plants and transmission systems interact. By simulating these complex interactions, engineers can identify potential stability issues before they occur in actual grid operations. This predictive capability is particularly valuable for large-scale power plants that serve critical loads or operate in interconnected grid networks.
Fault Condition Simulation
Power plants must demonstrate their ability to maintain stability during various fault conditions including short circuits, equipment failures, and transmission line disturbances. Regenerative grid simulators excel at creating controlled fault scenarios that allow comprehensive testing without risking actual grid infrastructure. These systems can generate fault conditions with precise timing and magnitude control, enabling engineers to evaluate protection system response and overall plant stability.
The fault simulation capabilities include modeling both symmetrical and asymmetrical fault conditions across different voltage levels. Engineers can program complex fault sequences that test cascading failure scenarios and evaluate the effectiveness of protection coordination schemes. This comprehensive fault testing ensures that power plants meet regulatory requirements while maintaining operational reliability.

Operational Benefits and Cost Advantages
Energy Efficiency and Cost Reduction
The regenerative nature of these simulators provides significant economic advantages over traditional testing methods. By recovering and recycling energy during testing operations, regenerative systems can reduce energy consumption by up to 90% compared to conventional load banks. This energy efficiency translates directly into lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact, making stability testing more sustainable and economically viable.
Long-term operational cost benefits extend beyond energy savings to include reduced maintenance requirements and extended equipment lifespan. The regenerative grid simulator technology typically requires less frequent calibration and maintenance compared to traditional testing equipment, resulting in lower lifecycle costs and improved testing availability.
Improved Testing Accuracy
Accuracy in stability testing directly impacts the reliability of power plant operations and grid stability assessments. Regenerative grid simulators provide superior measurement precision and control accuracy compared to conventional testing methods. The advanced feedback control systems maintain tight regulation of electrical parameters even under dynamic conditions, ensuring that test results accurately reflect actual power plant performance characteristics.
The enhanced accuracy extends to harmonic analysis capabilities where regenerative systems can generate and measure harmonic content with exceptional precision. This capability is crucial for evaluating power plant compatibility with modern grid conditions that include increasing levels of harmonic distortion from electronic loads and renewable energy systems. Accurate harmonic testing ensures compliance with grid codes and optimal power quality performance.
Integration with Modern Grid Technologies
Renewable Energy Integration Testing
As renewable energy sources become increasingly prevalent in power systems, stability testing must account for the unique characteristics of these generation technologies. A regenerative grid simulator can model the variable and intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, allowing power plants to test their response to rapid changes in grid conditions. This capability is essential for ensuring stable operation in grids with high renewable energy penetration.
The simulator technology enables comprehensive testing of power plant interactions with renewable energy systems including wind farms, solar installations, and energy storage systems. Engineers can evaluate how conventional power plants respond to sudden changes in renewable generation and test the effectiveness of grid stabilization measures. This integrated approach to stability testing ensures reliable grid operation as renewable energy adoption continues to expand.
Smart Grid Compatibility
Modern power grids increasingly incorporate smart grid technologies that require sophisticated communication and control capabilities. Regenerative grid simulators can integrate with smart grid systems to test advanced grid management functions including demand response, automatic generation control, and distributed energy resource coordination. This integration capability ensures that power plants remain compatible with evolving grid technologies.
The smart grid compatibility extends to testing communication protocols and cybersecurity measures that are critical for modern power plant operations. Regenerative systems can simulate cyber attacks and communication failures to evaluate power plant resilience and response capabilities. This comprehensive approach to testing ensures that power plants maintain stability even under adverse conditions that could affect smart grid operations.
Technical Specifications and Performance Parameters
Power Rating and Voltage Capabilities
Regenerative grid simulator systems are available in various power ratings ranging from laboratory-scale units to large industrial systems capable of testing major power plants. High-power systems can handle megawatt-level testing requirements while maintaining precise control over electrical parameters. The voltage capabilities typically span multiple voltage levels from low voltage distribution systems to high voltage transmission applications.
The technical specifications of regenerative systems include impressive dynamic response characteristics with rise times measured in microseconds and frequency response extending well beyond grid frequency ranges. These performance parameters enable accurate simulation of fast transient conditions and high-frequency phenomena that can affect power plant stability. The wide bandwidth capability ensures comprehensive testing coverage across all relevant frequency ranges.
Control System Architecture
The control system architecture of a regenerative grid simulator incorporates redundant processing units, high-speed analog-to-digital converters, and advanced communication interfaces. Multiple control loops operate simultaneously to maintain precise regulation of output parameters while monitoring system performance and safety conditions. The modular architecture allows for system expansion and customization based on specific testing requirements.
Advanced human-machine interfaces provide intuitive operation and comprehensive data visualization capabilities. Engineers can configure complex test sequences, monitor real-time performance, and analyze historical data through sophisticated software platforms. The integration of remote monitoring capabilities enables expert support and system optimization from any location, enhancing testing efficiency and reducing operational complexity.
Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
Planning and Site Preparation
Successful implementation of a regenerative grid simulator requires careful planning and site preparation to ensure optimal performance and safety. Site requirements include adequate electrical infrastructure, cooling systems, and physical space for equipment installation and operation. The planning process must consider future expansion needs and integration with existing testing facilities to maximize long-term value.
Environmental considerations play a crucial role in regenerative grid simulator installation and operation. These systems typically generate less heat and noise compared to traditional testing equipment, making them suitable for installation in various environments. However, proper ventilation and climate control remain important factors for maintaining equipment reliability and measurement accuracy over extended periods.
Training and Operational Procedures
Effective utilization of regenerative grid simulator technology requires comprehensive training for engineering and technical staff. Training programs must cover system operation, safety procedures, data analysis techniques, and maintenance requirements. The complexity of modern regenerative systems demands ongoing education to keep pace with technological advances and evolving testing standards.
Operational procedures for regenerative grid simulator systems emphasize safety, accuracy, and efficiency in testing operations. Standardized test procedures ensure consistent results and enable meaningful comparison of test data across different time periods and operating conditions. Documentation and record-keeping requirements support regulatory compliance and facilitate continuous improvement in testing methodologies.
Future Developments and Emerging Trends
Artificial Intelligence Integration
The future of regenerative grid simulator technology includes increasing integration with artificial intelligence and machine learning capabilities. AI-enhanced systems can automatically optimize test parameters, predict equipment behavior, and identify potential stability issues before they become critical problems. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast amounts of test data to identify patterns and trends that might not be apparent through traditional analysis methods.
Predictive maintenance capabilities represent another area where AI integration can significantly improve regenerative grid simulator performance and reliability. By analyzing operational data and equipment condition indicators, AI systems can predict when maintenance is needed and optimize maintenance schedules to minimize downtime. This proactive approach to maintenance ensures maximum testing availability and reduces lifecycle costs.
Advanced Communication Technologies
Emerging communication technologies including 5G networks and advanced cybersecurity protocols will enhance the capabilities of regenerative grid simulator systems. High-speed, low-latency communication enables real-time coordination between multiple testing systems and facilitates remote operation and monitoring capabilities. Enhanced cybersecurity measures ensure that testing operations remain secure even in interconnected environments.
The integration of cloud computing technologies allows for distributed data analysis and collaborative testing programs where multiple facilities can share test results and best practices. Cloud-based data storage and analysis platforms provide unlimited scalability for handling large volumes of test data while enabling advanced analytics and reporting capabilities. This connectivity enhances the value of individual regenerative grid simulator installations through shared knowledge and resources.
FAQ
What makes a regenerative grid simulator more effective than traditional testing equipment
A regenerative grid simulator offers superior effectiveness through its ability to recover and reuse energy during testing operations, reducing energy consumption by up to 90%. The dynamic response capabilities allow for more realistic simulation of actual grid conditions, while advanced control systems provide unprecedented accuracy in parameter regulation. The bidirectional energy flow and sophisticated feedback control enable comprehensive testing scenarios that traditional equipment cannot achieve.
How does regenerative technology impact testing accuracy and reliability
Regenerative technology significantly improves testing accuracy through precise control over electrical parameters and real-time feedback systems that maintain stability under dynamic conditions. The advanced digital signal processing and control algorithms ensure consistent performance across wide operating ranges. Reliability is enhanced through reduced thermal stress on components, lower maintenance requirements, and built-in redundancy features that prevent testing interruptions.
What are the key considerations for implementing a regenerative grid simulator system
Key implementation considerations include site preparation requirements such as adequate electrical infrastructure and cooling systems, staff training needs for operating complex control systems, and integration with existing testing facilities. Budget planning must account for initial equipment costs, installation expenses, and ongoing operational benefits. Regulatory compliance and safety requirements also play important roles in successful regenerative grid simulator implementation.
How does a regenerative grid simulator support renewable energy integration testing
Regenerative grid simulators excel at modeling the variable and intermittent characteristics of renewable energy sources, allowing comprehensive testing of power plant response to rapid changes in grid conditions. The systems can simulate complex interactions between conventional generation and renewable sources while testing grid stabilization measures. This capability ensures power plant compatibility with high renewable energy penetration scenarios and supports reliable grid operation as clean energy adoption expands.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Regenerative Grid Simulation Technology
- Enhanced Stability Testing Capabilities
- Operational Benefits and Cost Advantages
- Integration with Modern Grid Technologies
- Technical Specifications and Performance Parameters
- Implementation Strategies and Best Practices
- Future Developments and Emerging Trends
-
FAQ
- What makes a regenerative grid simulator more effective than traditional testing equipment
- How does regenerative technology impact testing accuracy and reliability
- What are the key considerations for implementing a regenerative grid simulator system
- How does a regenerative grid simulator support renewable energy integration testing