microgrid
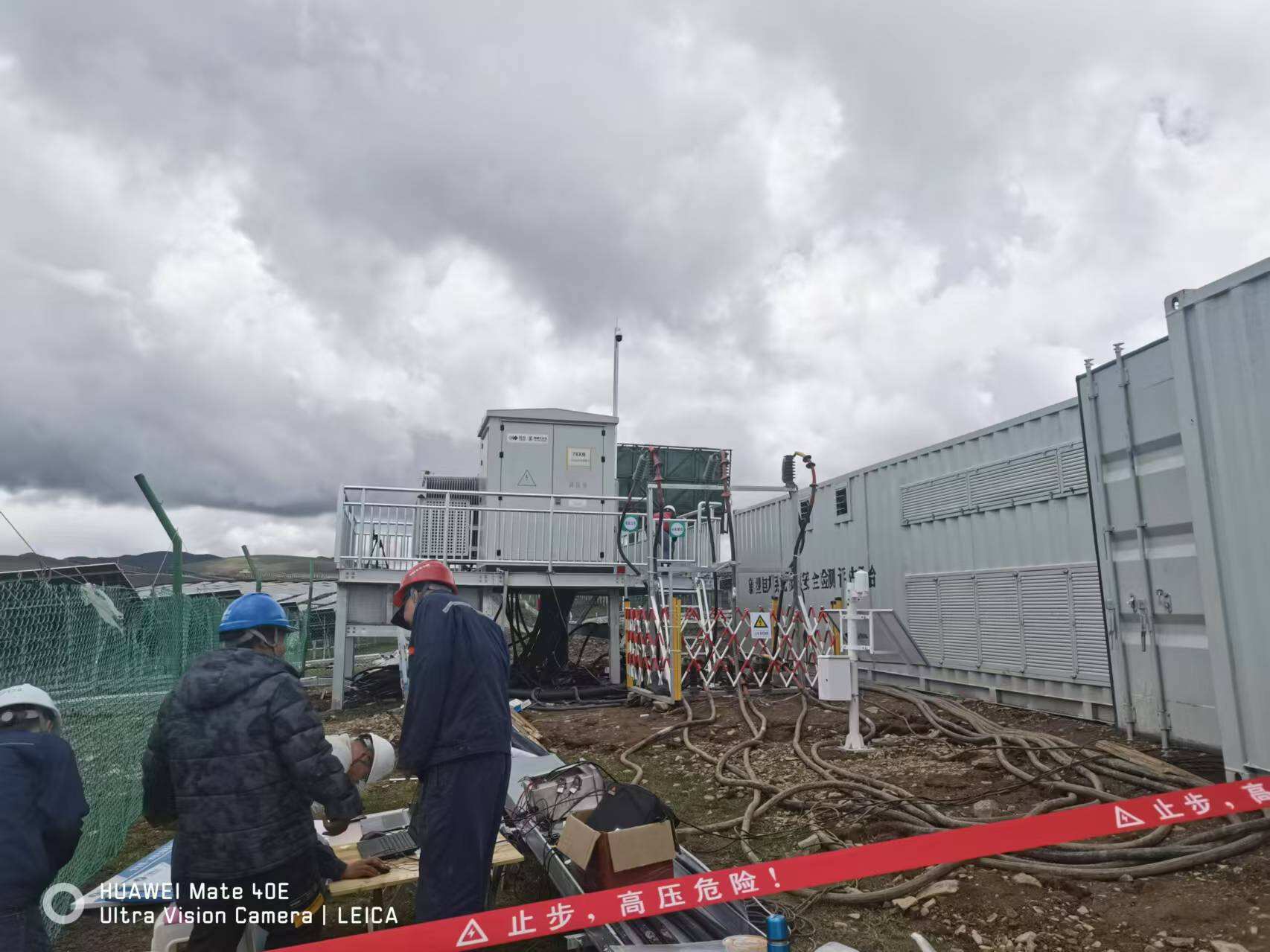
A microgrid is an advanced, localized energy system that operates as a single, controllable entity within a defined electrical boundary. This sophisticated infrastructure combines various power sources, including renewable energy, conventional generators, and energy storage systems, working in harmony to provide reliable electricity supply. The system can operate either connected to the main power grid or independently in island mode, offering unprecedented flexibility in power management. Microgrids incorporate smart technology and advanced control systems that automatically balance power supply and demand, optimize energy usage, and maintain stable operation. They integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines, while also accommodating traditional power sources. The technology enables real-time monitoring and response to changing energy needs, ensuring efficient distribution and consumption. Applications of microgrids span across various sectors, from powering remote communities and military installations to supporting critical facilities like hospitals and data centers. They also serve as resilient backup systems during grid outages and natural disasters, providing essential power continuity. In urban settings, microgrids can power entire neighborhoods or campus environments, while in industrial applications, they ensure reliable power for manufacturing processes.